关于C++对象布局 看了大佬的博客,大佬的博客过于久远格式比较清奇,我整理了,顺便改了程序能够在 64位机运行。
单一的一般继承
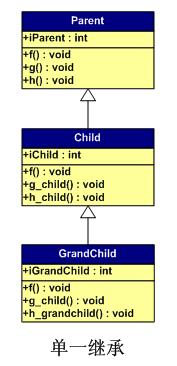
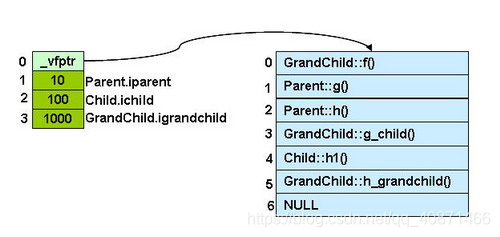
通俗的讲,一层层下去。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
using namespace std;
class Parent
{
public:
long iparent;//因为是64位机,所以改成了 long
Parent() : iparent(10) {}
virtual void f() { cout << " Parent::f()" << endl; }
virtual void g() { cout << " Parent::g()" << endl; }
virtual void h() { cout << " Parent::h()" << endl; }
};
class Child : public Parent
{
public:
long ichild;
Child() : ichild(100) {}
virtual void f() { cout << "Child::f()" << endl; }
virtual void g_child() { cout << "Child::g_child()" << endl; }
virtual void h_child() { cout << "Child::h_child()" << endl; }
};
class GrandChild : public Child
{
public:
long igrandchild;
GrandChild() : igrandchild(1000) {}
virtual void f() { cout << "GrandChild::f()" << endl; }
virtual void g_child() { cout << "GrandChild::g_child()" << endl; }
virtual void h_grandchild() { cout << "GrandChild::h_grandchild()" << endl; }
};
typedef void (*Fun)(void);
int main()
{
GrandChild gc;
long **pVtab = (long **)&gc;
Fun pFun;
cout << "[0] GrandChild::_vptr->" << endl;
for (int i = 0; (Fun)pVtab[0][i] != NULL; i += 2)
{
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][i];
cout << " [" << i << "] ";
pFun();
}
printf("start offet:%llx\n", pVtab);
cout << "[1] Parent.iparent = " << (long)((pVtab[1])) << endl;
cout << "[2] Child.ichild = " << (long)(pVtab[2]) << endl;
cout << "[3] GrandChild.igrandchild = " << (long)(pVtab[3]) << endl;
}
输出结果1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8[0] GrandChild::_vptr->
[0] GrandChild::f()
[2] Parent::h()
[4] Child::h_child()
start offet:7ffee4956f80
[1] Parent.iparent = 10
[2] Child.ichild = 100
[3] GrandChild.igrandchild = 1000
顺便我们用gdb 看一下。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22GNU gdb (Debian 7.12-6) 7.12.0.20161007-git
list
40 {
41 pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][i];
42 cout << " [" << i << "] ";
43 pFun();
44 }
45 printf("start offet:%llx\n", pVtab);
46 cout << "[1] Parent.iparent = " << (long)((pVtab[1])) << endl;
47 cout << "[2] Child.ichild = " << (long)(pVtab[2]) << endl;
48 cout << "[3] GrandChild.igrandchild = " << (long)(pVtab[3]) << endl;
49 }
p pVtab
$1 = (long **) 0x7fffffffcb90
x /10xg 0x7fffffffcb90
0x7fffffffcb90: 0x0000555555755ce0(你可以继续找下去可以找到具体函数地址) 0x000000000000000a(10)
0x7fffffffcba0: 0x0000000000000064(100) 0x00000000000003e8(1000)
0x7fffffffcbb0: 0x000000000000008e 0x000055555555509a
0x7fffffffcbc0: 0x00007fffffffcb90 0x0000000655554bf0
0x7fffffffcbd0: 0x00007fffffffccc0 0x0000000000000000
多重继承
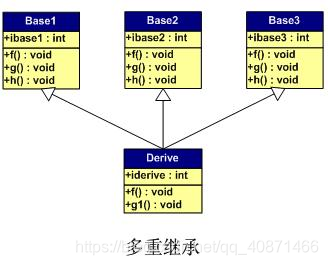
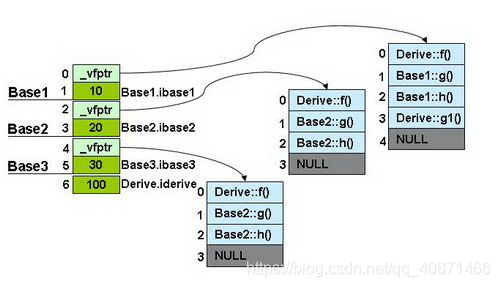
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
using namespace std;
class Base1
{
public:
long ibase1;
Base1() : ibase1(0x10) {}
virtual void f() { cout << "Base1::f()" << endl; }
virtual void g() { cout << "Base1::g()" << endl; }
virtual void h() { cout << "Base1::h()" << endl; }
};
class Base2
{
public:
long ibase2;
Base2() : ibase2(0x20) {}
virtual void f() { cout << "Base2::f()" << endl; }
virtual void g() { cout << "Base2::g()" << endl; }
virtual void h() { cout << "Base2::h()" << endl; }
};
class Base3
{
public:
long ibase3;
Base3() : ibase3(0x30) {}
virtual void f() { cout << "Base3::f()" << endl; }
virtual void g() { cout << "Base3::g()" << endl; }
virtual void h() { cout << "Base3::h()" << endl; }
};
class Derive : public Base1,
public Base2,
public Base3
{
public:
long iderive;
Derive() : iderive(0x100) {}
virtual void f() { cout << "Derive::f()" << endl; }
virtual void g1() { cout << "Derive::g1()" << endl; }
};
typedef void (*Fun)(void);
int main()
{
Derive d;
long **pVtab = (long **)&d;
Fun pFun;
cout<<hex;
cout << "[0] Base1::_vptr->" << endl;
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][0];
cout << " [0] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][1];
cout << " [1] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][2];
cout << " [2] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][3];
cout << " [3] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][4];
cout << " [4] ";
cout << pFun << endl;
cout << "[1] Base1.ibase1 = " << (long)(pVtab[1]) << endl;
long s = sizeof(Base1) / 8;
cout << "[" << s << "] Base2::_vptr->" << endl;
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[s][0];
cout << " [0] ";
pFun();
cout << " [1] ";
pFun=(Fun)pVtab[s][1];
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[s][2];
cout << " [2] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[s][3];
cout << " [3] ";
cout << pFun << endl;
cout << "[" << s + 1 << "] Base2.ibase2 = " << (long)(pVtab[s + 1]) << endl;
s = s + sizeof(Base2) / 8;
cout << "[" << s << "] Base3::_vptr->" << endl;
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[s][0];
cout << " [0] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[s][1];
cout << " [1] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[s][2];
cout << " [2] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[s][3];
cout << " [3] ";
cout << pFun << endl;
s++;
cout << "[" << s << "] Base3.ibase3 = " << (long)pVtab[s] << endl;
s++;
cout << "[" << s << "] Derive.iderive = " << (long)pVtab[s] << endl;
}
运行结果1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20[0] Base1::_vptr->
[0] Derive::f()
[1] Base1::g()
[2] Base1::h()
[3] Derive::g1()
[4] 1//这个表示最后一个
[1] Base1.ibase1 = 10
[2] Base2::_vptr->
[0] Derive::f()
[1] Base2::g()
[2] Base2::h()
[3] 1
[3] Base2.ibase2 = 20
[4] Base3::_vptr->
[0] Derive::f()
[1] Base3::g()
[2] Base3::h()
[3] 0
[5] Base3.ibase3 = 30
[6] Derive.iderive = 100
用GDB看看1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23-exec p pVtab
$1 = (long **) 0x7fffffffcb80
-exec x /10xg 0x7fffffffcb80
0x7fffffffcb80: 0x0000555555756c50 0x0000000000000010
0x7fffffffcb90: 0x0000555555756c80 0x0000000000000020
0x7fffffffcba0: 0x0000555555756ca8 0x0000000000000030
0x7fffffffcbb0: 0x0000000000000100 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffffffcbc0: 0x000055555555583e 0x00007fffffffcb80
-exec x /10xg 0x0000555555756c50
0x555555756c50 <_ZTV6Derive+16>: 0x000055555555583e 0x00005555555555be
0x555555756c60 <_ZTV6Derive+32>: 0x00005555555555f6 0x0000555555555882
0x555555756c70 <_ZTV6Derive+48>: 0xfffffffffffffff0 0x0000555555756d38
0x555555756c80 <_ZTV6Derive+64>: 0x000055555555587b 0x000055555555568c
0x555555756c90 <_ZTV6Derive+80>: 0x00005555555556c4 0xffffffffffffffe0
-exec x /10xg 0x000055555555583e (不知道为啥其他查看其他几个虚表,和这个值不一样,但是也指向这个函数)
0x55555555583e <Derive::f()>: 0x10ec8348e5894855 0x57358d48f87d8948
0x55555555584e <Derive::f()+16>: 0x18083d8d48000001 0x48fffff453e80020
0x55555555585e <Derive::f()+32>: 0x201791058b48c289 0xe8d78948c6894800
0x55555555586e <Derive::f()+48>: 0x48c3c990fffff45e 0xef8348c3eb20ef83
0x55555555587e <_ZThn16_N6Derive1fEv+3>: 0xe589485590bdeb10 0xf87d894810ec8348
重复继承
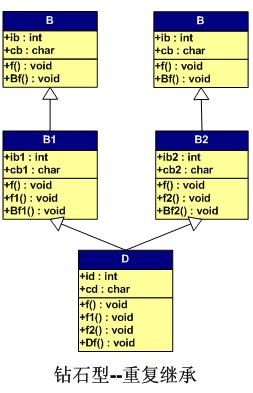
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
using namespace std;
class B
{
public:
long ib;
char cb;
public:
B() : ib(0), cb('B')
{
}
virtual void
f()
{
cout << "B::f()" << endl;
}
virtual void Bf() { cout << "B::Bf()" << endl; }
};
class B1 : public B
{
public:
long ib1;
char cb1;
public:
B1() : ib1(11), cb1('1')
{
}
virtual void
f()
{
cout << "B1::f()" << endl;
}
virtual void f1() { cout << "B1::f1()" << endl; }
virtual void Bf1() { cout << "B1::Bf1()" << endl; }
};
class B2 : public B
{
public:
long ib2;
char cb2;
public:
B2() : ib2(12), cb2('2')
{
}
virtual void
f()
{
cout << "B2::f()" << endl;
}
virtual void f2() { cout << "B2::f2()" << endl; }
virtual void Bf2() { cout << "B2::Bf2()" << endl; }
};
class D : public B1,
public B2
{
public:
long id;
char cd;
public:
D() : id(100), cd('D')
{
}
virtual void
f()
{
cout << "D::f()" << endl;
}
virtual void f1() { cout << "D::f1()" << endl; }
virtual void f2() { cout << "D::f2()" << endl; }
virtual void Df() { cout << "D::Df()" << endl; }
};
typedef void (*Fun)(void);
int main()
{
long **pVtab = NULL;
Fun pFun = NULL;
D d;
pVtab = (long **)&d;
cout << "[0] D::B1::_vptr->" << endl;
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][0];
cout << " [0] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][1];
cout << " [1] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][2];
cout << " [2] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][3];
cout << " [3] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][4];
cout << " [4] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][5];
cout << " [5] 0x" << pFun << endl;
cout << "[1] B::ib = " << (long)pVtab[1] << endl;
cout << "[2] B::cb = " << static_cast<char>((long)(pVtab[2])) << endl;
cout << "[3] B1::ib1 = " << (long)pVtab[3] << endl;
cout << "[4] B1::cb1 = " << (static_cast<char>((long)(pVtab[4]))) << endl;
cout
<< "[5] D::B2::_vptr->" << endl;
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[5][0];
cout << " [0] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[5][1];
cout << " [1] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[5][2];
cout << " [2] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[5][3];
cout << " [3] ";
pFun();
pFun = (Fun)pVtab[5][4];
cout << " [4] 0x" << pFun << endl;
cout << "[6] B::ib = " << (long)pVtab[6] << endl;
cout << "[7] B::cb = " << (static_cast<char>((long)pVtab[7])) << endl;
cout << "[8] B2::ib2 = " << (long)pVtab[8] << endl;
cout << "[9] B2::cb2 = " << (static_cast<char>((long)pVtab[9])) << endl;
cout << "[10] D::id = " << (long)pVtab[10] << endl;
cout << "[11] D::cd = " << (static_cast<char>((long)pVtab[11])) << endl;
}
输出结果1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23[0] D::B1::_vptr->
[0] D::f()
[1] B::Bf()
[2] D::f1()
[3] B1::Bf1()
[4] D::f2()
[5] 0x1
[1] B::ib = 0
[2] B::cb = B
[3] B1::ib1 = 11
[4] B1::cb1 = 1
[5] D::B2::_vptr->
[0] D::f()
[1] B::Bf()
[2] D::f2()
[3] B2::Bf2()
[4] 0x0
[6] B::ib = 0
[7] B::cb = B
[8] B2::ib2 = 12
[9] B2::cb2 = 2
[10] D::id = 100
[11] D::cd = D
GDB调试
1 | x /12x 0x7fffffffcb60 |
虚拟继承
大佬偷懒了,那我们完了啊。
对于这个虚拟继承,和64位机好像有点不一样,我也不知道为啥。
如果有人看懂了回来私信我(留个言也行)。告诉我为啥。
我贴一个自己的实验。不保证正确性。